If you’ve ever studied a language in your life then you’ve certainly heard of conditionals. You know, another one of those grammar rules that make things complicated. But what if you could also make grammar fun? Would that make things less complicated? Would you enjoying learning a bit more? If grammar was fun, then I would certainly enjoy studying much more! That’s exactly what conditionals do… they allow for a little more creativity and thinking in a different way. So how exactly is this possible? Before we take a look at how to use the conditional tense in English first break it down and see what conditionals are.
Imagine, if you could have one superpower what would it be?
If you could instantly learn a language what would it be? (other than English of course!)
What would you do with 10 billion dollars?
If you could change one thing in your life, what would it be?
Interesting questions, right? Well as it turns out, these questions are all what we call in English grammar as conditionals.
What are conditionals?
The conditional tense in English is simply the structure of questions and answers that allow you to tell a story. They are ways of showing actions that happen, have happened, that will happen or that would have happened if you do, will do or did something. The conditional allows you to express exactly what you mean and exactly when it did or will happen. Think of a time machine. Having a time machine would be amazing, right!? You could go back and forth in time and change or create whatever you wanted. That’s kind of what conditionals do, but with language. Exciting, right?
So let’s take a look at how to recognize the structure of conditionals and finally get to seeing how to use the conditional tense in English.
Different uses of the conditional tenses in English
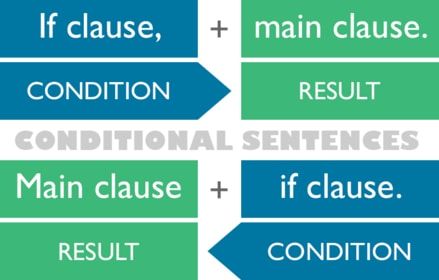
Typically when the word “if” is in a sentence, it’s a conditional. There are many ways to say and write conditionals, but they must always contain the word if. The clauses can be in a different order yet mean the same thing. For example,
If he sleeps a lot, then he is rested.
He is rested if he sleeps a lot.
These two sentences have the exact same meaning, they are just structured differently, yet they both contain the word if. This is your biggest clue in recognizing all the conditional tenses in English. There are four different conditional tenses so let’s look at how to use each of them.

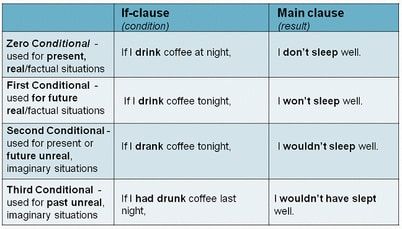
How to use the Zero Conditional
Zero conditional is quite common and a lot more simple than it seems. This tense is used to describe or talk about something that is a general truth, such as a fact. Think of this as the scientific conditional. These are certain to be true. For example,
“If you freeze water, it turns to ice.”
“Ice melts if you heat it.”
“Water boils if it is heated to 100 degrees.”
There will always be the conditional or ‘if’ clause and the result clause. The structure is:
If + present simple (If this happens) / present simple (that thing happens)
How to use the First Conditional
The first conditional is used to describe something that probably will happen if you do something else. This is for something that is realistically likely to happen. It requires the “if” clause to describe the condition that needs to take place, and is followed by main clause that tells you what will likely happen. For example,
“If I have enough money, I’ll buy some shoes.”
“If it rains, I won’t go to the park.”
“If I see him, I’ll tell him.”
If + present simple / will + infinitive
What’s your English level?
Find out by completing one of our level tests!
What’s your English level?
Find out by completing one of our level tests!
How to use the Second Conditional
The second conditional is used to describe something that isn’t likely to take place, and describes a situation that is different from reality. This is the one you can have a lot of fun with, because they are not real events. You can invent anything in the world that you want.
There are two uses for this conditional but the structure is the same for both.
If + past simple / would + infinitive
Firstly, we use the second conditional for events in the future that are most likely not going to be true. This is where we can invent our dreams! For example,
“If I wont the lottery, I would buy a private airplane.”
“Most people would travel all over the world if they were rich.”
“If aliens came to Earth, there would be chaos.”
Secondly, we use this conditional to talk about something in the present that is impossible, because it’s not true. For example,
“If I had extra time, I would go to the gym.”
“If I were you, I wouldn’t talk to her anymore.”
“If I had his number, I would give it to you.”
How to use the Third Conditional

The third conditional is to describe something that didn’t happen but could have happened with the right conditions. This is used to talk about something that you wish had or hadn’t happened in the past. Remember that time machine? This is the conditional tense that allows you to really go back in time and (pretend to) change whatever you want!
If + past perfect / would + have + past participle
“If I left earlier, then I wouldn’t have missed my flight.”
“He would have become a lawyer if he had gone to law school.”
“If she had studied more, she would have passed her exam.”
Once you break it down, conditionals are actually quite simple! They allow you to be creative, to tell a story, to  share obvious facts and even to have a language time machine! Conditionals make the English language more varied and interesting. There are many activities to help you practice conditionals, such as storytelling with friends. Or try speaking with a native English speaker. There’s no better way to learn and practice than that.
share obvious facts and even to have a language time machine! Conditionals make the English language more varied and interesting. There are many activities to help you practice conditionals, such as storytelling with friends. Or try speaking with a native English speaker. There’s no better way to learn and practice than that.
Now that you know how to use the conditional tense in English, try it out! Have fun!