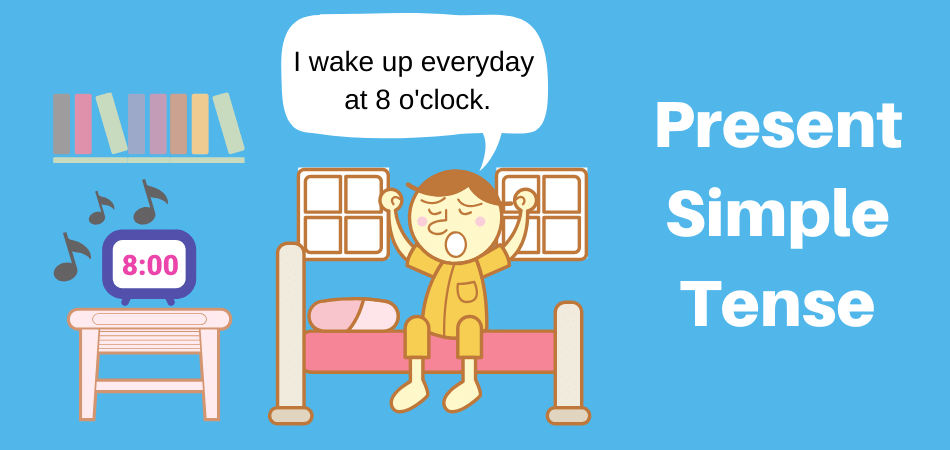
In this article, we will describe the present simple explained in pictures in an easy way to understand. The present simple is used to talk about things in general. We use it to describe actions that happen frequently or situations that are generally true. When you finish this post, you might want to take a look at present simple rules with state verbs here.
For example:

- Doctors work in hospitals. [true in general]
- The doctor starts work at 9:00. [happens all the time]
Present simple explained in pictures: Use the plain infinitive with “I”, “you”, “we” and “they”.
This tense is constructed by using the plain infinitive, the infinitive without “to”, when the subject is “I” (also known as the 1st person singular), “you” (the 2nd person singular / plural), “we” (the 1st person plural) or “they” (the 3rd person plural).
This aspect of the present simple explained in an image:

For example:
- I work as a shop assistant.
- You work as a cashier.
- We work at weekends.
- They work together.
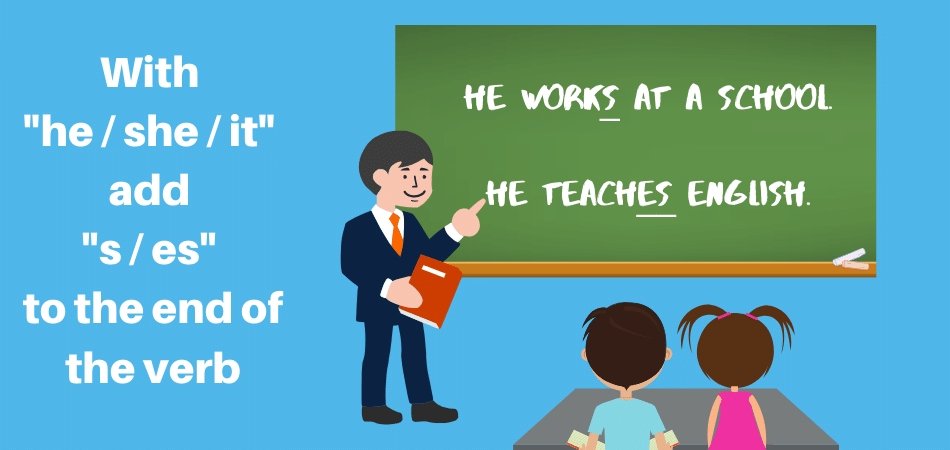
With “He”, “She” and “It” add “s” or “es” to the verb
In the 3rd person singular, “he / she / it,” the verb ending changes (conjugates) to agree with the subject. In English, this change only happens with these three subjects, making verbs in the present tense quite easy to learn compared to other languages. To use 3rd person singular subjects in the present simple, just add “s” or “es” to the end of the plain infinitive verb.
This picture explains the third person verb conjugation:
For example:
- He works at a school.
- He teaches English.
Pronunciation of “s” ending in the 3rd person singular
Although this ending is simple to use, the pronunciation can change depending on the last sound of the original verb. For most verbs the “s” ending is pronounced as a vibrating ‘z’ sound. However, in verbs ending with “p/t/k/f” sounds, the “s” ending is pronounced with a soft ‘s’ sound.
For example:
- He runs every day. [pronounced with vibrating ‘z’]
- She mops the floor. [ ends in p sound, [pronounced with soft ‘s’]
- He sits at the computer for long hours. [ends in t sound, pronounced with soft ‘s’]
- She cooks every day. [ends in k sound, pronounced with soft ‘s’]
- He laughs loudly. [ends in f sound, pronounced with soft ‘s’]
Verbs that end in “ss/sh/ch/tch/x” add “es” in the 3rd person singular – Present simple explained in pictures
Since it can be difficult to pronounce the letters above together with “s,” English chooses to add “es” instead. Remember that “es” also adds and extra syllable and so the pronunciation changes too, sounding like ‘iz’.
See this image for an easy explanation:

For example:
- She misses home. [misses = 2 syllables – “mis” + “ses”]
- He washes the dishes. [washes = 2 syllables – “wa” + “shes”]
- It searches for information online. [searches = 2 syllables – “sear” + “ches”]
- He watches a lot of TV series. [watches = 2 syllables – “wat” + “ches”]
- She mixes the ingredients together. [mixes = 2 syllables – “mi” + “xes”]
Verbs that end in “o” also add “es” in the 3rd person singular
There are not many verbs that end in “o” in English but they also use “es” when “he / she / it” is the subject. However in this case, “es” does not add an extra syllable.
This picture explains this aspect of the present simple:

For example:
- He goes to school. [to go (1 syllable) > +es > goes (1 syllable)]
- She does yoga on Wednesdays. [to do (1 syllable) > +es > does (1 syllable)]
- It echoes inside the cave. [to echo (2 syllables) > +es > echoes (2 syllables)]
Present simple explained in pictures: “-y” verbs in the 3rd person singular add “ies” if the previous letter is a consonant.
Verbs that end in a consonant + “y” use “es” in the 3rd person singular and also change spelling. The “y” is replaced with “i” and “es” is added as seen above. On the other hand, if the letter before “y” is a vowel, the verb adds the regular “s” ending instead and there is no spelling change. In both cases the number of syllables does not increase.
Present simple explained in pictures:
 For example:
For example:
She studies hard. [to study (2 syllables) > change y to i, +es > studies (2 syllables)]
He tries new restaurants all the time. [to try (1 syllable) > change y to i, +es > tries (1 syllable)]
She enjoys horror movies. [to enjoy (2 syllables) > no change, +s > enjoys (2 syllables)]
He buys sport magazines. [to buy (1 syllable) > no change, +s > buys (1 syllable)]
Images describing negatives and questions in the present simple: use the auxiliary verb “do”
For present simple negative sentences or questions, English uses the verb “do” together with the main verb. Verbs that “help” the main verb like this are called auxiliary verbs. Remember, as we saw above “do” ends in an “o” and so uses the “es” ending in the third person singular, becoming “does” when “he / she / it” is the subject. In negative sentences, “do / does” is followed by “not” and then the main verb. “Do / does not” can also be shortened to “don’t / doesn’t.”
The negative use of the present simple is explained in this picture:

For example:
We do not work at a school. [subject, auxiliary+not, main verb]
OR
We don’t work at a school.
He does not speak English. [subject, auxiliary+not, main verb]
OR
He doesn’t speak English.
To form questions, the word order changes. “Do/does” is used at the start, followed by the subject and then the main verb. We also use “ do/does” again in the reply.
This image explains questions in the present simple:

For example:
Do you work here? [auxiliary, subject, main verb]
- Yes, we do.
Does he speak English? [auxiliary, subject, main verb]
- No, he doesn’t.
For more info about questions check out this article here: https://breakintoenglish.com/blog/how-to-learn-english/how-to-ask-questions-in-english/
The present simple and adverbs of frequency explained in pictures
As the present simple tense is used to talk about things that happen repeatedly it is often combined with adverbs of frequency. These are words that tell us how often something is done.
Adverbs of frequency in the present simple explained in a picture:

For example:
I always wake up at 8 o’ clock. [100% of the time]
It usually rains in autumn. [More true than not true]
They often go to the cinema. [More true than not true]
She sometimes reads books. [50% of the time]
He rarely drinks tea. [More untrue than true]
We never go to the theatre. [0% of the time]
Summary
To recap, we’ve seen that the present simple is used to make generalisations and talk about things that happen frequently, often together with adverbs of frequency (e.g. always, sometimes, never). It uses the plain infinitive form of the verb, without “to” e.g. “to work,” however, there are spelling and pronunciation changes when the subject is in the 3rd person, e.g. “he / she / it works.” This is a very common tense and is found in media all around us. Check out the songs below that use the present simple tense and leave a comment to let us know of any more you can think of!
Florence + The Machine – You’ve Got The Love
Alesha Dixon – The Boy Does Nothing
P.s. Here is a famous film clip that uses the present simple together with adverbs of frequency. Do recognise which film it is from?
For other examples of grammar explained in pictures, check out our GRAMMAR INDEX here.

This article was written by Break Into English’s blog contributor Ilaria Marazzina.